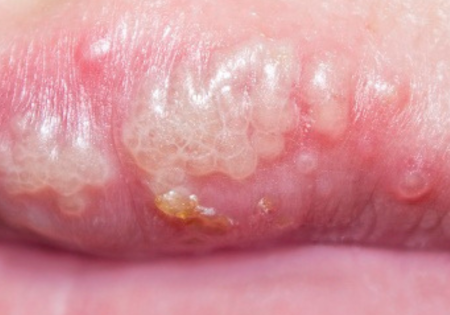
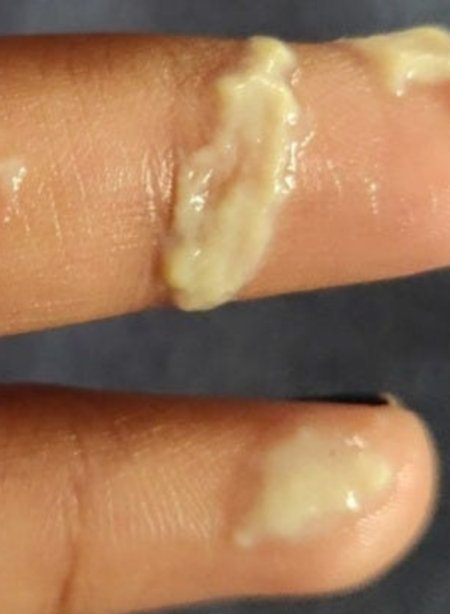
A sexually transmitted infection (STI) known as gonorrhea is brought on by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. It is typically transmitted by unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact with an infected individual. It can infect both men and women.
The urethra, rectum, throat, and reproductive systems are frequently impacted by gonorrhea, which can cause symptoms including painful or burning urination, atypical vaginal discharge, or even no symptoms at all.
Serious side effects from gonorrhea include infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and an elevated risk of HIV transmission if treatment is not received. Usually, a medical practitioner will prescribe antibiotics as part of the treatment.
The risk of gonorrhea transmission can be decreased by taking preventive steps, such as having safe sexual relations and getting frequent STI testing.
Signs of Gonorrhea:
- Unusual Genital Discharge: For both men and women, an unusual discharge from the genitalia is one of the main indicators of gonorrhea.
This discharge can be thick or thin in men and is usually white, yellow, or greenish in appearance.
Vaginal discharge in women can be hazy or yellow in color. - Pain or Burning Sensation During Urination: Gonorrhea patients frequently experience pain or a burning sensation during urination.
Inflammation of the urethra in men and the cervix in women is the cause of this symptom. - Testicles that are painful or swollen (in men): Men who have gonorrhea may have testicular pain or edema.
This condition, called epididymitis, is brought on by inflammation of the sperm-carrying tube, the epididymis. - Abnormal Bleeding (In Women): Gonorrhea-infected women may have abnormal vaginal bleeding during their periods or during sexual activity.
Inflammation of the cervix or other reproductive organs may be the cause of this bleeding. - Oral Gonorrhea-Related Sore Throat: Gonorrhea can be spread by oral sex, which can result in a throat infection.
Oral gonorrhea can cause swelling lymph nodes in the neck, swallowing difficulties, and sore throats.
Extra Information:
- It’s crucial to remember that gonorrhea symptoms can differ greatly from person to person and that some people may not even exhibit any symptoms.
- Serious side effects from untreated gonorrhea might include infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and an elevated risk of HIV transmission.
- Gonorrhea must be diagnosed and treated quickly in order to minimize problems and slow the infection’s spread.
It’s critical to get tested and treated by a doctor if you think you might have gonorrhea or have been exposed to the virus.
Conclusion:
Early detection and treatment of gonorrhea depend on the ability to recognize its symptoms. By being aware of these signs, people can get medical attention as soon as possible and stop the virus from spreading to other people. For an assessment and proper management, speak with a healthcare provider if you encounter any of the following symptoms or have concerns about gonorrhea.